
Types of Networking devices
Networking devices are essential for connecting networks. As computer networks expand in size and complexity, the need for these devices becomes more critical. The most commonly used types of networking devices include:
Repeaters
Hubs
Bridges
Routers
The purpose of networking devices is to connect network by using nodes , these devices provide more nodes for the systems to be connected. In this way , these devices extend the network over the long distance and localize the networks. These devices can merge the existing networks and these are also helpful to diagnosed the problems by isolating the system.
Repeaters
Repeaters are located in the physical layer of the OSI model and provide a solution for two common issues. When the length of the cable increases, the signal tends to weaken and deteriorate. In such cases, repeaters help by retransmitting the signal and directing it toward the destination.
However, a drawback of repeaters is that when data reaches one port of the repeater, it may be sent to other ports, regardless of whether it should go there or not.
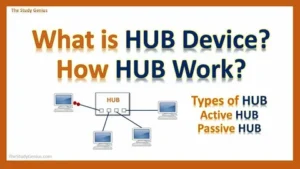
Hub
The multi-port repeaters known as hubs. These are very common devices. It serves as center as we see in star Topology. Hub is generally known as multi-port repeater or Ethernet or constructor. Hub and repeater can face the problem of traffic collision , these devices are non-filtering devices.
Bridge
A bridge is used to address issues related to traffic collisions and signal strength. It reduces the likelihood of traffic collisions and minimizes unnecessary traffic by dividing the network into segments. The bridge facilitates packet transmission between two networks.
Operating at the Data Link layer, a bridge is more efficient than a hub. It works well when the traffic between two segments is light. However, if the traffic between segments becomes too heavy, the bridge may slow down communication.
Routers
A router is another important networking device that operates at the third layer of the OSI model, the Network layer. It makes intelligent decisions to determine the best path for data delivery across the network.
Routers perform several key functions:

- Path Determination
- Path Communication
- Addressing Network and Nodes
Routers are effective in managing heavy traffic and are distinct from bridges in their use of network addresses. Unlike bridges, which operate on MAC addresses, routers use IP addresses to forward data. Routers are typically used to connect multiple networks, with each network having a unique and specific network identifier.
Networking devices are hardware components that enable communication and data transfer between computers, servers, and other devices within a network. These devices play a crucial role in establishing, managing, and optimizing network connections. There are several types of networking devices, each serving a specific function:
Switch
A switch operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) and connects devices within a single network or LAN. It forwards data packets based on MAC addresses and helps manage traffic within the network, creating efficient communication between devices.
- Bridge:
A bridge divides a network into segments, reducing traffic collisions and improving signal strength. It operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) and forwards data between two network segments, helping to reduce congestion and optimize network performance. - Repeater:
A repeater extends the range of a network by amplifying or regenerating weak signals. It operates at the Physical layer (Layer 1) and retransmits signals to maintain signal integrity over long distances. - Gateway:
A gateway acts as a translator between different network protocols. It enables communication between networks that use different protocols and is often used to connect a private network to the internet. - Access Point (AP):
An access point provides wireless connectivity to devices within a network. It allows Wi-Fi-enabled devices, such as laptops and smartphones, to connect to a wired network.
Each of these networking devices plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient data communication across various types of networks.

